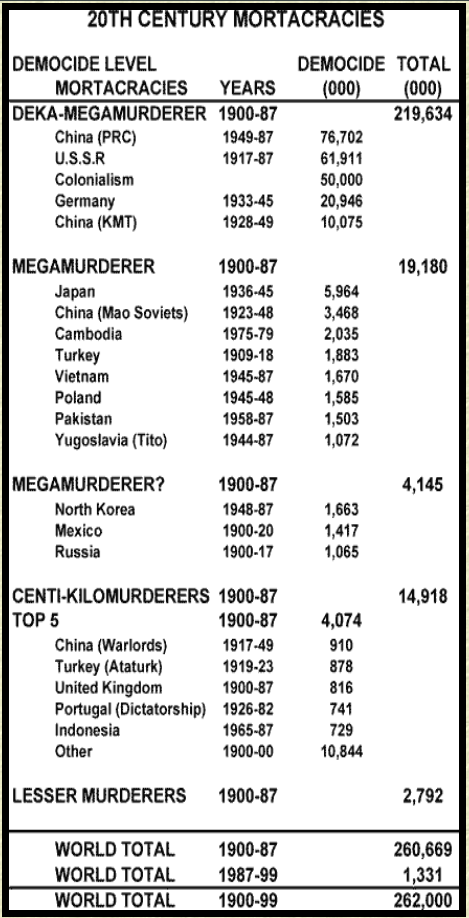
- Democide: This term refers to the murder of any person or people by a government, including genocide, politicide, and mass murder. Estimates by Rudolph Rummel suggest that governments were responsible for the deaths of 262 million people in the 20th century, significantly more than battle-related deaths.
- Civilian Casualties in Military Operations: Governments engaging in military operations are often accountable for civilian deaths resulting from those operations. The U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) releases annual reports detailing civilian casualties in connection with military operations. These reports are required by law to list operations resulting in confirmed or suspected civilian casualties, the methods used to assess these casualties, and efforts to reduce them. The reports also discuss processes for offering condolences and payments to victims and their families.
- Public Health Policies and Crises: Government actions and inaction’s can impact public health and mortality rates. Examples include regulations that hinder the provision of healthcare services, cuts to essential programs like Medicaid or foreign aid that supports global health initiatives. The effectiveness of a government’s response to public health crises, such as pandemics, can have a significant impact on mortality rates.
- Transparency and Reporting: The level of transparency in government data collection and reporting of deaths, particularly during crises like pandemics, can impact public understanding of the situation and the government’s response. Concerns have also been raised regarding the release of death records and autopsy reports due to the sensitive personal information they may contain.
In other words they try and cover up their crimes by any means possible so you don’t blame the Guilty, by blaming the Victims.
1. 169,202,000 Murdered: Summary and Conclusions [20th Century Democide]
I BACKGROUND
2. The New Concept of Democide [Definition of Democide]
3. Over 133,147,000 Murdered: Pre-Twentieth Century Democide
II 128,168,000 VICTIMS: THE DEKA-MEGAMURDERERS
4. 61,911,000 Murdered: The Soviet Gulag State
5. 35,236,000 Murdered: The Communist Chinese Ant Hill
6. 20,946,000 Murdered: The Nazi Genocide State
7. 10,214,000 Murdered: The Depraved Nationalist Regime
III 19,178,000 VICTIMS: THE LESSER MEGA-MURDERERS
8. 5,964,000 Murdered: Japan’s Savage Military
9. 2,035,000 Murdered: The Khmer Rouge Hell State
10. 1,883,000 Murdered: Turkey’s Genocidal Purges
11. 1,670,000 Murdered: The Vietnamese War State
12. 1,585,000 Murdered: Poland’s Ethnic Cleansing
13. 1,503,000 Murdered: The Pakistani Cutthroat State
14. 1,072,000 Murdered: Tito’s Slaughterhouse
IV 4,145,000 VICTIMS: SUSPECTED MEGAMURDERERS
15. 1,663,000 Murdered? Orwellian North Korea
16. 1,417,000 Murdered? Barbarous Mexico
17. 1,066,000 Murdered? Feudal RussiaReferences Index
IMPORTANT NOTE: Among all the democide estimates appearing in this book, some have been revised upward. I have changed that for Mao’s famine, 1958-1962, from zero to 38,000,000. And thus I have had to change the overall democide for the PRC (1928-1987) from 38,702,000 to 76,702,000. Details here.
I have changed my estimate for colonial democide from 870,000 to an additional 50,000,000. Details here.
Thus, the new world total: old total 1900-1999 = 174,000,000. New World total = 174,000,000 + 38,000,000 (new for China) + 50,000,000 (new for Colonies) = 262,000,000.
Just to give perspective on this incredible murder by government, if all these bodies were laid head to toe, with the average height being 5′, then they would circle the earth ten times. Also, this democide murdered 6 times more people than died in combat in all the foreign and internal wars of the century. Finally, given popular estimates of the dead in a major nuclear war, this total democide is as though such a war did occur, but with its dead spread over a century.
- Books on Democide
- Lethal Politics: Soviet Genocides and Mass Murders 1917-1987, Rutgers, New Jersey: Transaction Publishers, 1990: Preface, References, and all tables of estimates, calculations and sources for each historical period.
- China’s Bloody Century: Genocide and Mass Murder Since 1900. Rutgers, New Jersey: Transaction Publishers, 1991: Preface, Chapter 1, Methods Appendix, References, and all tables of estimates, calculations and sources for each historical period.
- Democide: Nazi Genocide and Mass Murder. Rutgers, New Jersey: Transaction Publishers, 1992: Preface, Chapter 1, References, and the summary overall table of estimates, calculations and sources.
- Death by Government: Genocide and Mass Murder in the Twentieth Century, New Jersey: Transaction Publishers, 1994: Preface; Chapters 1, 2, and 3; References; and the summary table for each megamurderer.
- Statistics of Democide. Center on National Security and Law, University of Virginia, 1997: entire. Republished by Lit Verlag, MŸster, Germany in 1998 and distributed in North America by Transaction Publishers.
- Lethal Politics: Soviet Genocides and Mass Murders 1917-1987, Rutgers, New Jersey: Transaction Publishers, 1990: Preface, References, and all tables of estimates, calculations and sources for each historical period.
- Definitions
- The new concept of democide: Definition and qualifications [1]
- Article: What is Genocide?
- Democide versus genocide: which is what?
- Chapter: 1900-1987: 169,198,000 murdered [1]
- Article: pilot study: war isn’t this century’s biggest killer
- References: overall sources of estimates/quotes/information [5]
- Table: summary by regime [5]
- Figure: democide year-by-year and war and rebellion-dead [5]
- What governments murdered how many?
- Table: summary of megamurderers–regimes that murdered 1,000,000 people or more [1]
- Chapter: the centi-kilo murderers–regimes that murdered 100,000 to 999,999 people or more [5]
- Tables: estimates, calculations, and sources, by states and by quasi-states [5]
- Chapter: the lesser murderers–regimes that murdered less than 100,000 people [5]
- Chapter: democide in totalitarian states: mortacracies and megamurderers–an annotated bibliography
- Chapter: the Holocaust in comparative perspective
- Paper: democide since World War II
- Chapter: the social field of democide [5]
- Tables: descriptive statistics among types of democide; their intercorrelations, and factors [5]





0 Comments